Configuring Firewalls
As a admin user, learn how VADAAR uses the network and which ports should be opened to allow for full functionality.
Overview
VADAAR allows for centralised control of all Senders/Viewers in your environment. To facilitate this, the Senders/Viewers connect directly to the VADAAR instance with a long running socket to allow for bidirectional communication.
To stream media between different VADAAR endpoints uses the WebRTC protocol. The applications will use the VADAAR instance as a signalling server to facilitate the exchanging of information, however once this initial handshake is complete, all media is sent directly to the other endpoint using peer-2-peer networking.
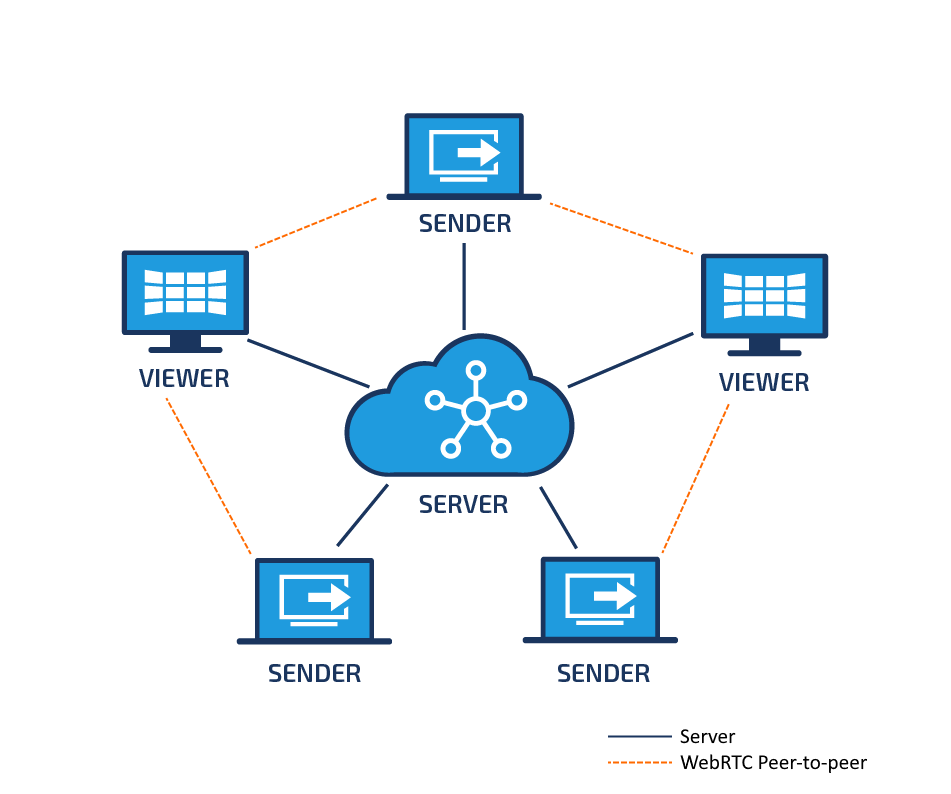
Ports
| Application | Protocol | Source Ports | Destination Ports |
|---|---|---|---|
| VADAAR | TCP | 8442,8443 | |
| Sender | TCP | 8442,8443 | |
| Sender | UDP | Ephemeral ports | Ephemeral ports |
| Viewer | TCP | 8442,8443 | |
| Viewer | UDP | Ephemeral ports | Ephemeral ports |
Ephemeral Ports
VADAAR Sender/Viewer and the web browser utilise the Operating Systems Ephemeral Port range when starting to stream the media using the network. Each connection will use a new random Ephemeral port pair to send/receive data. A list of default ephemeral ports can be found below:
| OS | Ports |
|---|---|
| Windows | 49152-65535 |
| Linux | 32768-61000 |